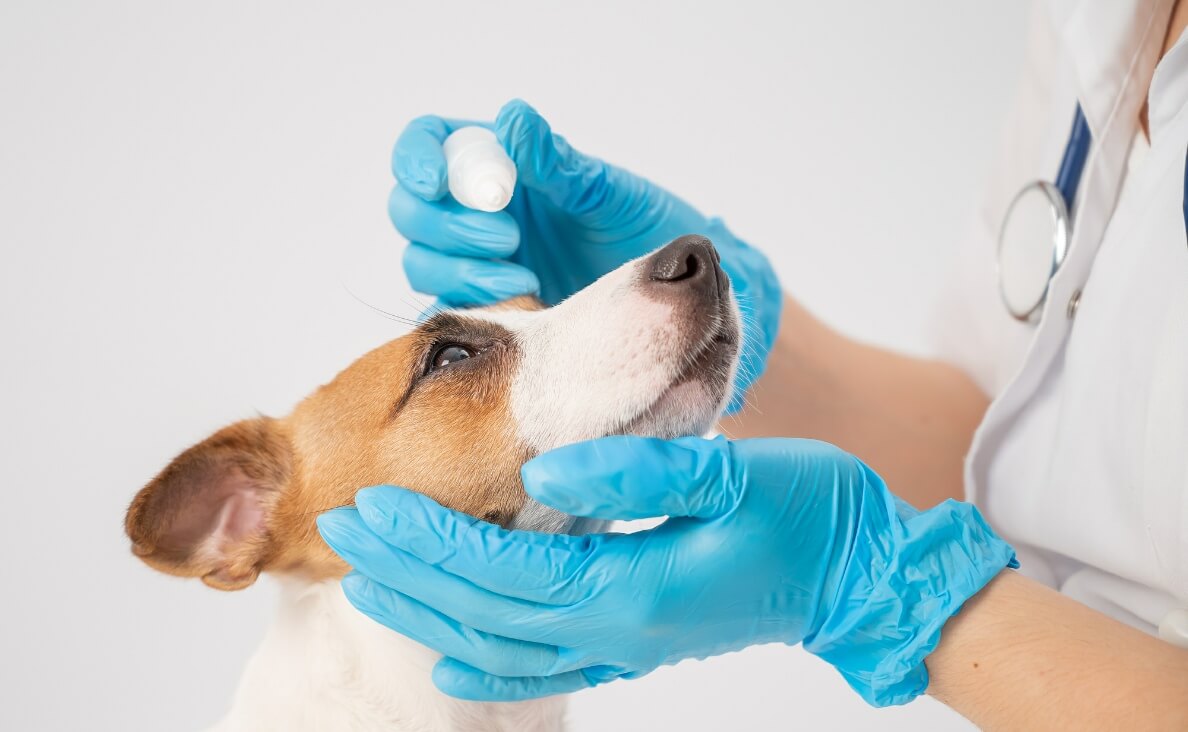
Dog eye infections are a common yet concerning issue for many dog parents. These infections can cause significant discomfort and even lead to more serious health problems if not treated promptly. Understanding the signs, causes, and treatment options for dog eye infections is crucial for maintaining your furry family member’s overall health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what dog eye infections are, how they are diagnosed, various treatment options, and preventive measures to keep your dog’s eyes healthy and infection-free.
What Are Dog Eye Infections?
Dog eye infections occur when harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, invade the eye or surrounding tissues. These infections can affect different parts of the eye, including the conjunctiva (the membrane lining the eyelids), the cornea (the clear, outer layer of the eye), and even the deeper structures of the eye. There are several types of dog eye infections, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment requirements.
Bacterial eye infections are the most common and often result from injuries or foreign bodies entering the eye. Symptoms typically include redness, swelling, and a yellow or green discharge. Viral eye infections, on the other hand, are usually associated with other illnesses, such as canine distemper or canine herpesvirus. These infections often present with watery discharge, redness, and discomfort. Fungal infections, though less common, can occur in dogs with compromised immune systems or those exposed to certain environmental conditions.
Understanding the different types of dog eye infections is the first step in recognizing and addressing this issue. By being aware of the symptoms and potential causes, you can take prompt action to ensure your dog’s eye health is restored as quickly as possible.
Related: 9 Common Eye Issues in Dogs
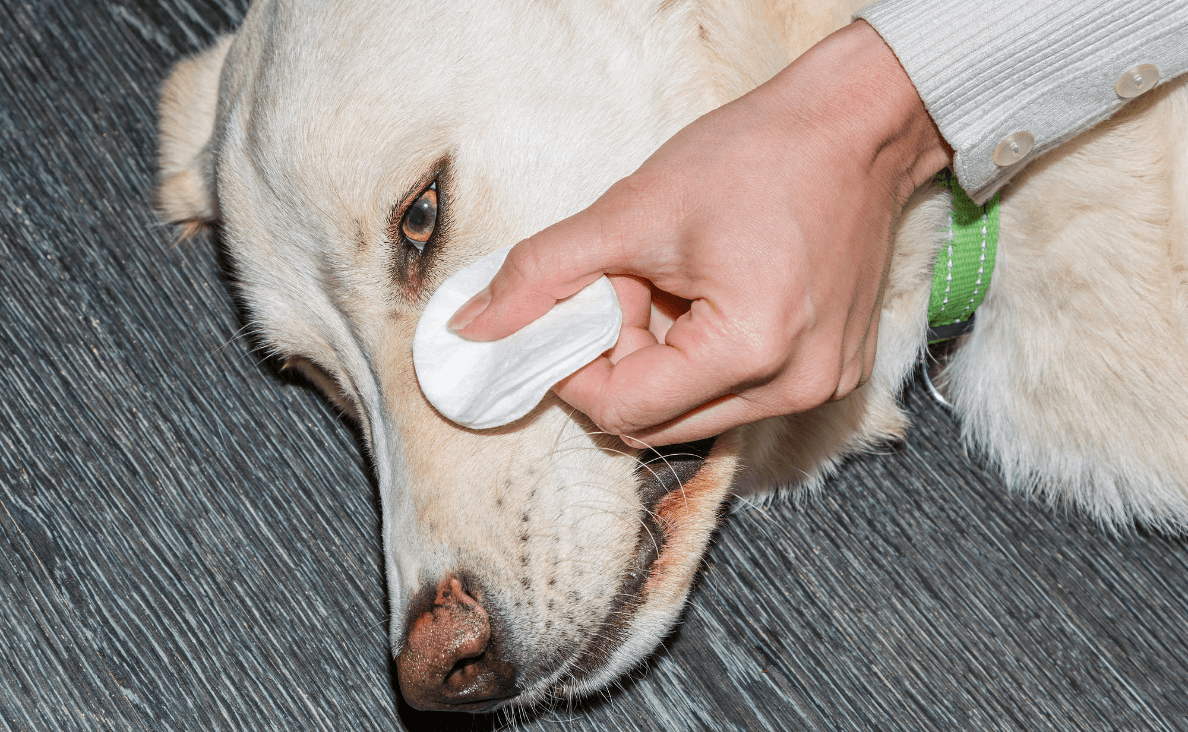

Causes of Dog Eye Infections
There are numerous causes of dog eye infections, ranging from environmental factors to underlying health conditions. One of the most common causes is the presence of foreign bodies in the eye, such as dirt, dust, or plant material. These foreign particles can irritate the eye, leading to inflammation and infection if not promptly removed.
Allergies are another significant cause of dog eye infections. Just like humans, dogs can suffer from allergies to pollen, mold, dust mites, and other environmental allergens. Allergic reactions can cause the eyes to become red, itchy, and watery, creating a conducive environment for infections to develop.
Related: Help Your Dog Fight Seasonal Allergies
Injuries to the eye, whether from rough play, fights with other animals, or accidents, can also lead to infections. Even a small scratch or abrasion can provide an entry point for bacteria or viruses, resulting in an infection. It’s essential to monitor your dog’s eyes for any signs of injury and seek veterinary care if needed.
Certain underlying health conditions can predispose dogs to eye infections. For example, dogs with diabetes are more susceptible to infections due to their compromised immune systems. Additionally, breeds with protruding eyes, such as Pugs and Bulldogs, are at higher risk because their eyes are more exposed and prone to injury.
Environmental factors, such as exposure to contaminated water or living in unsanitary conditions, can also contribute to the development of eye infections. Ensuring that your dog’s living environment is clean and free from potential irritants can go a long way in preventing infections.
By understanding the various causes of dog eye infections, you can take proactive measures to minimize your dog’s risk and keep their eyes healthy.
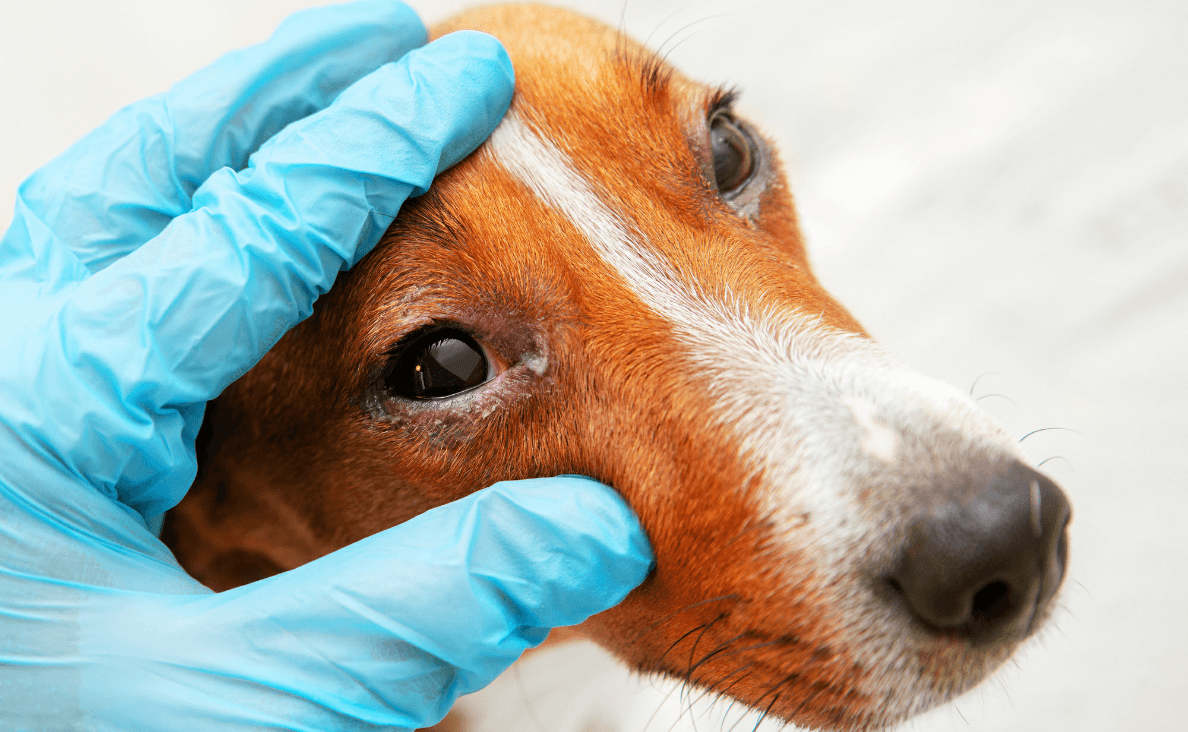
Diagnosing Dog Eye Infections
Diagnosing dog eye infections typically involves a thorough examination by a veterinarian. It’s crucial to seek professional help if you notice any signs of an eye infection in your dog, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and promote faster recovery.
During the examination, the veterinarian will assess the eye for signs of redness, swelling, discharge, and any visible injuries. They may also use special diagnostic tools and tests to determine the cause and extent of the infection. One common test is the fluorescein stain test, which involves applying a fluorescent dye to the eye’s surface. This dye helps highlight any corneal ulcers or scratches that may not be visible to the naked eye.
In some cases, the veterinarian may take a sample of the eye discharge to identify the specific type of microorganism causing the infection. This sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis, allowing the veterinarian to prescribe the most effective treatment based on the identified pathogen.
It’s important to provide the veterinarian with as much information as possible about your dog’s symptoms, recent activities, and any potential exposure to allergens or irritants. This information can help narrow down the possible causes and guide the diagnostic process.
Early and accurate diagnosis of dog eye infections is essential for effective treatment. By seeking veterinary care at the first sign of an infection, you can ensure that your dog receives the appropriate care and enjoys a swift recovery. 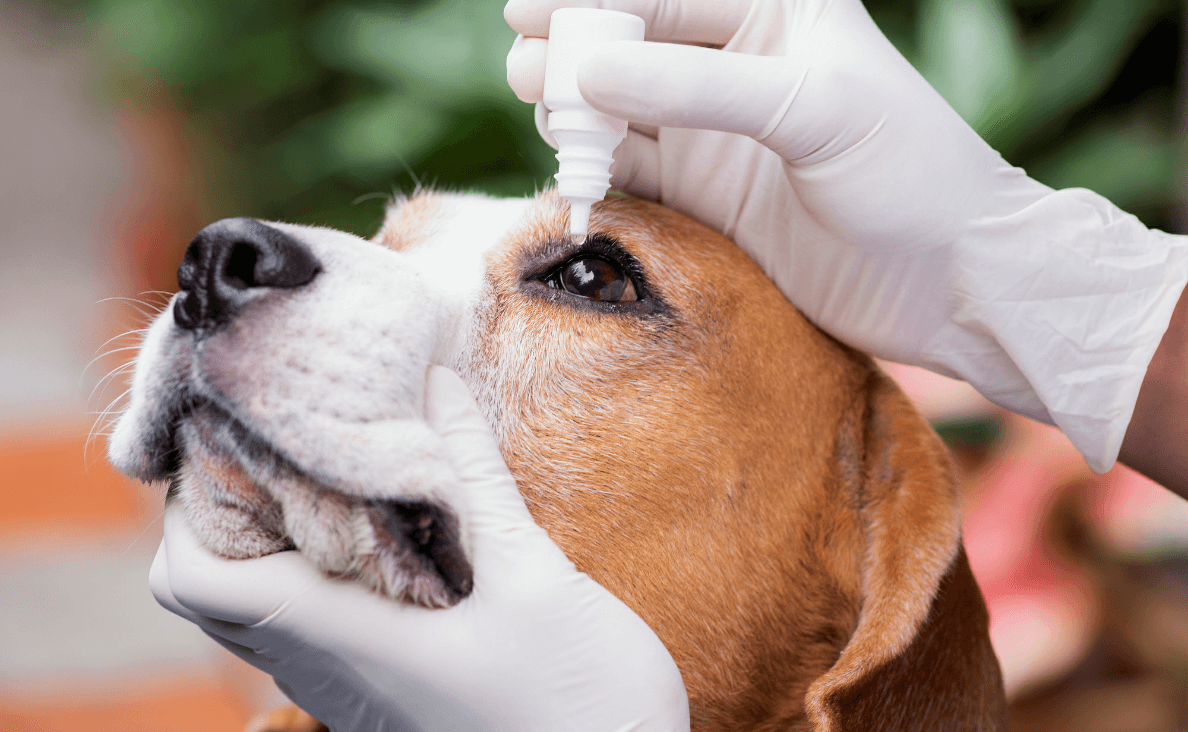
Treatment Options for Dog Eye Infections
Treating dog eye infections involves a combination of veterinary care and home remedies. The specific treatment plan will depend on the type and severity of the infection, as well as your dog’s overall health and any underlying conditions.
Medications:
One of the most common treatments for bacterial eye infections is the use of antibiotics. These can be administered as eye drops, ointments, or oral medications, depending on the infection’s location and severity. It’s crucial to follow the veterinarian’s instructions carefully and complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
Viral eye infections, such as those caused by canine distemper or herpesvirus, may require antiviral medications. These medications help manage the symptoms and reduce the viral load, but supportive care is often needed to help the dog’s immune system fight off the infection.
Fungal eye infections are treated with antifungal medications, which can be challenging to administer and may require a longer treatment duration. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue and prevent the spread of the infection.
Home Remedies:
In addition to medications, several home remedies can help alleviate the symptoms of dog eye infections and support the healing process. Warm compresses applied to the affected eye can help reduce swelling and discomfort. Simply soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring out the excess, and gently hold it against your dog’s eye for a few minutes.
Saline rinses are another effective home remedy for dog eye infections. You can purchase sterile saline solution from a pharmacy or make your own by dissolving a teaspoon of salt in a cup of boiled, cooled water. Use a clean dropper or syringe to gently flush the eye with the saline solution, helping to remove debris and soothe irritation.
Preventative Measures:
Preventing dog eye infections involves maintaining good hygiene and taking proactive steps to minimize exposure to potential irritants and pathogens.
Regular grooming is also essential, especially for breeds with long hair that can irritate the eyes. Trim the hair around the eyes to prevent it from getting into the eyes and causing infections. Additionally, ensure your dog receives a balanced diet and regular veterinary check-ups to maintain their overall health and immune system.
By combining veterinary care with appropriate home remedies and preventative measures, you can effectively treat and prevent dog eye infections, ensuring your dog’s eyes remain healthy and comfortable.

Home Care for Dogs with Eye Infections
Caring for a dog with an eye infection at home requires patience and diligence. Following your veterinarian’s instructions and implementing supportive home care measures can significantly improve your dog’s comfort and aid in their recovery.
One of the most important aspects of home care is keeping the affected eye clean. Use a damp, clean cloth to gently wipe away any discharge from the eye, being careful not to touch the eye itself. This helps prevent the buildup of bacteria and reduces the risk of the infection spreading.
Administering medications as prescribed is crucial for treating dog eye infections. Whether it’s eye drops, ointments, or oral medications, follow the veterinarian’s instructions carefully. If you’re using eye drops or ointments, make sure to wash your hands before and after application to prevent contamination. Hold your dog’s head steady and gently pull down the lower eyelid to create a small pocket for the medication. Administer the prescribed amount and allow your dog to blink, distributing the medication across the eye.
In addition to medications, providing a comfortable and stress-free environment can help your dog recover more quickly. Ensure your dog has a clean and quiet place to rest, away from potential irritants such as dust, smoke, or strong odors. Monitor your dog’s behavior and symptoms closely and report any changes or concerns to your veterinarian.
It’s also essential to prevent your dog from scratching or rubbing their eyes, which can worsen the infection and cause further damage. Consider using an Elizabethan collar (cone) to prevent your dog from reaching their eyes with their paws. Regularly check the collar to ensure it’s not causing any additional discomfort or irritation.
By implementing these home care measures, you can support your dog’s recovery and help them feel more comfortable during the treatment process.

Preventing Dog Eye Infections
Preventing dog eye infections involves a combination of good hygiene practices, regular veterinary care, and minimizing exposure to potential irritants and pathogens. Here are some practical tips to help keep your dog’s eyes healthy and infection-free.
Regular Check-Ups:
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for maintaining your dog’s overall health and catching any potential issues early. During these visits, the veterinarian can examine your dog’s eyes and identify any signs of infection or underlying conditions that may predispose them to eye problems.
Good Hygiene:
Keeping your dog’s eyes clean is crucial for preventing infections. Regularly clean your dog’s face and trim the hair around their eyes to prevent it from getting into the eyes and causing irritation.
Avoid Irritants:
Minimize your dog’s exposure to environmental irritants such as dust, smoke, chemicals, and allergens. If your dog has known allergies, work with your veterinarian to develop a management plan that includes avoiding allergens and possibly using medications to control allergic reactions.
Balanced Diet:
A balanced diet that provides all the necessary nutrients is essential for maintaining your dog’s overall health and immune system. A healthy immune system can better fight off infections and prevent eye problems. Consult your veterinarian to ensure your dog is receiving a nutritionally balanced diet suitable for their age, breed, and health status.
Protective Measures:
In environments where your dog is likely to encounter potential eye irritants or injuries, consider using protective measures such as dog goggles. These can be particularly useful for dogs that spend a lot of time outdoors, especially in areas with a lot of dust, debris, or water.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your dog’s risk of developing eye infections and ensure their eyes remain healthy and comfortable.

Conclusion
Dog eye infections are a common yet treatable issue that requires prompt attention and care. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dog eye infections, you can take proactive steps to ensure your dog’s eye health is maintained. Regular veterinary check-ups, good hygiene practices, and minimizing exposure to potential irritants are essential for preventing infections.
If you suspect your dog has an eye infection, seek veterinary care immediately to ensure a prompt and accurate diagnosis. With the right treatment and home care, your dog can recover quickly and enjoy healthy, infection-free eyes.
Has your dog experienced an eye infection? Share your experiences and tips in the comments below…

 How to Prevent and Treat Motion Sickness in Dogs
How to Prevent and Treat Motion Sickness in Dogs 7 Creative Ways to Keep Your Dog Hydrated
7 Creative Ways to Keep Your Dog Hydrated Treat Your Disabled Dog with Integrative Medicine
Treat Your Disabled Dog with Integrative Medicine Why Dogs Excessively Lick Their Paws and How to Help
Why Dogs Excessively Lick Their Paws and How to Help What Every Dog Owner Should Know About Canine Influenza (Dog Flu)
What Every Dog Owner Should Know About Canine Influenza (Dog Flu)






Leave a Reply